Wellbeing and Positive Psychology
Key Kupu
What is Psychology? Post-war, mental illness getting from left to right. How can people flourish?
Once you are flourishing, how can you sustain that? Intrinsic words of motivation, Happiness, Self Efficacy, Optimism, Satisfaction, Creativity, Forgiveness, engagement.
Psychological Science is how Humans can flourish and wellbeing - Positive Psychology.
Wellbeing - connecting with nature, Social, Physical, Mental, acceptance of changes, Self-care and caring for others.
Flourishing Schools
- Walls
- Playground
- Assembly
- Classrooms
Positive Psychology Essentials
- We react more strongly to bad news than good news
- We have a negative bias
- Intentionally increasing the prevalence of positive emotions can improve wellbeing.
- Can respond to negative emotions and build resources
- If you have positive emotions, you are more creative
- If you are more negative, then you will be more critical
- Positive emotions we do better with connecting with others
- Increase cortisol and endorphins
- Positive emotions impact our relationships
- Positive emotions have more connections
Getting Granular
- Emotional literacy helps to name our emotions more accurately
- Increases resilience and supports relationships
Emotional Regulation
- Laughter
- Keeping the cork on the bottle, suppress it (Avoid feeling bad; don't want to deal with it). This builds the emotion and makes it stronger.
- Awareness and relating to that emotion more healthily - what is the stress telling me about this thing, and what shall I do about that. This is a motivator to take some action.
The ABC Model
- ABC - A = Activating - B = Belief C += Consequence
- A = Activating (Going into RED lockdown)
- B = What do we belief
- C = Stressed, concerned
Flow Theory
- Educational theories about learning and how we can use this in the classroom learning
- Everything falls into place - The challenge of the task you are doing matches the skill level you will flow.
- If you can make the task higher and more challenging
- To meet the flow - get students tasks to match their skills level so that they are engaged
- This is why scaffolding is very important
- The task to easy content in control and bored
- Too hard - students are disengaged
- Do activities that build a sense of cultural identity |
How can Flow Theory work for me/us?
- Having the lesson planned and following the plan
- Making learning visible for all students on Hapara and the Sites for dept
- Be a reflective teacher and keep a log of what's going well and what needs improvement next time. A place to write down stories, thoughts and reactions of students. Are the students happy, engaged, intrigued and positive?
- Students voice at the start, middle and end of the course
- Make learning fun through competition, relating the tasks to real life. Embed literacy short tasks and look back and praise students.
- Identify low ability students earlier on
- Scaffolding and creating resources for those students
In Teenagers, especially if:
- Promotes savouring
- Counters entitlement
- Inhibits social comparison - stops us from wishing
- Regulate your emotions - an option maybe change your environment - can be a good thing for our emotional wellbeing
Emotions and the Brain
The brain is compartmentalised for our understanding, but in reality, all the parts work in complex, intertwined ways. The largest section of the brain and closest to the surface is the Cerebrum (suh-REE-bruhm) or Cortex. This is often broken down into lobes or sections of the brain: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobes, and occipital lobe. The frontal lobe is at the front of the head and is responsible for planning, organisation, logical thinking, reasoning, and managing emotions. This is the part you will hear about most regarding the expression and regulation of emotions and behaviours. It is also known as the “higher brain”, “rational brain”, or the “upstairs brain”.
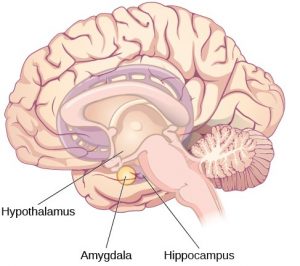 If we then jump to the brain's centre, we find some strangely named parts that play a big role in emotions. The Amygdala (uh-MIG-duh-luh) is a group of cells that interprets the emotional meaning of everything that happens to you. If the amygdala interprets something as threatening, it sends messages to another structure called the Hypothalamus (HI-pO-thal-a-mus), which controls the release of hormones into the body to get you ready for a fight-or-flight response. The fight-or-flight response happens when our bodies tense up, become more alert, and are ready for action to either escape (flight) or defend ourselves (fight). Finally, another structure called the Hippocampus (hip-uh-KAM-pus) organises memories so the amygdala can interpret an event. These three structures are part of what we call the “emotional brain” or “downstairs brain” and activate strong emotions and urge. This part of the brain can sometimes overreact (think of a child in a tantrum, or even our own reaction when the kids start fighting with each other), so needs a helping hand from the “rational brain” frontal lobes to settle down.
If we then jump to the brain's centre, we find some strangely named parts that play a big role in emotions. The Amygdala (uh-MIG-duh-luh) is a group of cells that interprets the emotional meaning of everything that happens to you. If the amygdala interprets something as threatening, it sends messages to another structure called the Hypothalamus (HI-pO-thal-a-mus), which controls the release of hormones into the body to get you ready for a fight-or-flight response. The fight-or-flight response happens when our bodies tense up, become more alert, and are ready for action to either escape (flight) or defend ourselves (fight). Finally, another structure called the Hippocampus (hip-uh-KAM-pus) organises memories so the amygdala can interpret an event. These three structures are part of what we call the “emotional brain” or “downstairs brain” and activate strong emotions and urge. This part of the brain can sometimes overreact (think of a child in a tantrum, or even our own reaction when the kids start fighting with each other), so needs a helping hand from the “rational brain” frontal lobes to settle down.
Reward
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter and is a motivator - get it when we expect something good to happens
- Feels good, great, nice, ecstatic, joyful.....dopamine
- Helpful for:
- Brain stimulation - gamers etc
- My students are inquisitive
- The say sure I got onto this tasks and I am now onto the next one for coding...
- Students show agency over their learning...wanting to lead, by showing what they want to do and just go and do things without being pushed or told what to do
- Feeling good after the gym
- Looking forward to a holiday
Minimise the Negative - Accentuate the Positive
- If the Ration is 5-1 five posotives ti one negative - long term relationships will flourish
- Teacher - student relationships - Do an inquiry of what are my ratio's of P's and N's with students
Taming the Four horseman
- Criticism - Negatives judgements
- Contempt - Eye rolling treating with disrespect, disgust, ridicule
- Defensiveness - Deflecting, blame or...
- Stonewalling - Withdrawing, shutting down etc
Active Constructive Responding
- Action and Constructive
- Listening
- Be authentic
- Empathise
- That's awesome; tell me a bit more...
- Ask questions after being positive
- We sometimes get caught in other thoughts
- Amplify the good news
- Make good news even better for that person
Growth Mindset
Neuroplasticity
- The routine of clapping and clicking
Resilience
- Strength
- Progress
- Push forward no matter what
- Hold the weight and keep going
- Bouncing back
- Retaining and keep working extra things and challenges develop
Caution with Grit
- Grit - Professor Angela Duckworth, UPenn
- Passion and perseverance for a long term Goal
- Ability and be mindful for other options - can be misused
- Sometimes preserving and working hard is not the best thing to do; we may need to reassess our goals
- Focus on long term goal
- Teach delay gratification - this is more likely to be successful but does not factor in the social-economic status of the family or whanau.
- Work now and feel and celebrate the reward later, acknowledging and validating.
Intrinsic v Extrinsic Motivation
- Continuum of motivation - not motivated, do it if I have to it = extrinsic motivation rather than Intrinsic the reason for doing this, see the value and benefit helping me and others etc.
- The 7 why's
- Why is it important to do that thing? Keep asking why?
- Tag onto the task you enjoy - don't like ironing, so put on a podcast etc.






